-
Top 5 Ways AI Is Transforming Healthcare DataSecurity
Top 5 Ways AI Is Transforming Healthcare DataSecurity Image Source: Pexels The effects of artificial intelligence on healthcare are profound. The same is true for healthcare data protection. AI technologies spot cyber dangers in healthcare systems quickly. They fortify data encryption and make access controls smarter. AI also speeds up the response to security breaches.… →

-
Top 5 Reasons Customers Love Botanical Wellness
Top 5 Reasons Customers Love Botanical Wellness Image Source: Pexels Over recent years, botanical wellness products have been rather popular and have become a mainstay in homes that value health all around. These plant-based medicines maximize the inherent power of herbs, flowers, roots, and other plant components used historically for millennia in many different civilizations.… →

-
A Code Implementation to Use Ollama through Google Colab and Building a Local RAG Pipeline on Using DeepSeek-R1 1.5B through Oll…
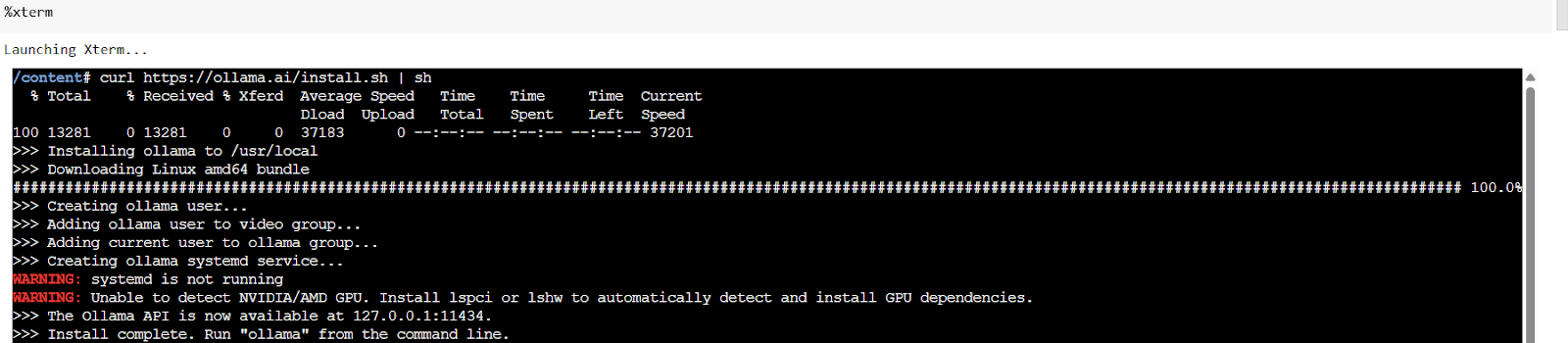
A Code Implementation to Use Ollama through Google Colab and Building a Local RAG Pipeline on Using DeepSeek-R1 1.5B through Ollama, LangChain, FAISS, and ChromaDB for Q&A In this tutorial, we’ll build a fully functional Retrieval-Augmented Generation () pipeline using open-source tools that run seamlessly on Google Colab. First, we will look into how to… →
-
This AI Paper Introduces Inference-Time Scaling Techniques: Microsoft’s Deep Evaluation of Reasoning Models on Complex Tasks…
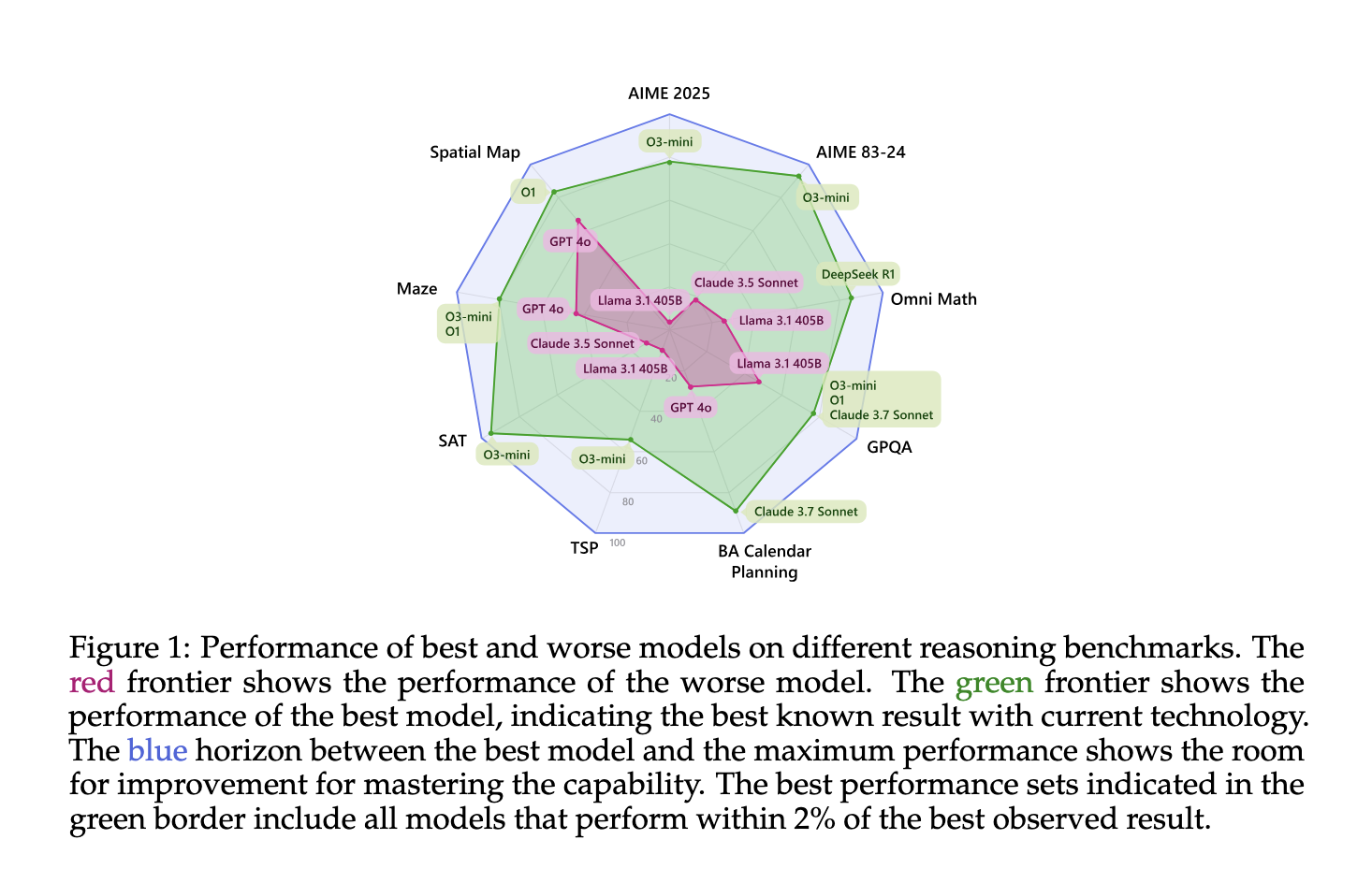
This AI Paper Introduces Inference-Time Scaling Techniques: Microsoft’s Deep Evaluation of Reasoning Models on Complex Tasks Large language models are often praised for their linguistic fluency, but a growing area of focus is enhancing their reasoning ability—especially in contexts where complex problem-solving is required. These include mathematical equations and tasks involving spatial logic, pathfinding, and… →
-
Urologists’ Estimation of Online Support Group Utilization Behavior of Their Patients With Newly Diagnosed Nonmetastatic Prostate Cancer in Germany: Predefined Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial
CONCLUSIONS: Physicians are more aware of F2FGs than OSGs. Before COVID-19, F2FGs played a minor role. One out of 4 patients used OSGs. One-third considered them helpful for treatment decision-making. OSG use rarely affects the final treatment decision. Urologists significantly underestimate OSG use by their patients. Peer-to-peer support is more likely to be received by… →
-
Personalized Alzheimer’s Risk Reduction Software Improves Calculated Alzheimer’s Risk: A Digital, Decentralized, Randomized Controlled Trial (P1-3.004)
CONCLUSIONS: RetainYourBrain effectively promotes behavior change in lifestyle domains linked to dementia risk. This innovative software offers a convenient, automated and cost-effective method for lowering AD risk that can be implemented more widely than otherwise possible in traditional, face-to-face health care encounters (ClinicalTrials.gov/NCT06027320). Disclaimer: Abstracts were not reviewed by Neurology® and do not reflect the… →

-
Impact of Lemborexant on Daytime Sleepiness/Alertness in Participants With Comorbid Insomnia and Mild Obstructive Sleep Apnea (P9-4.004)
CONCLUSIONS: While the sample size was too small to detect statistical differences, a greater percentage of participants with COMISA experienced improvements in morning sleepiness across the treatment period with LEM versus PBO. These data align with previous findings that LEM does not affect tasks requiring morning alertness. Disclosure: Margaret Moline has received personal compensation for… →
