-
Hitachi Vantara vs Siemens: Energy & Asset AI That Boosts Product Margins
Hitachi Vantara leverages industrial IoT and analytics for smarter asset management in sectors like transportation Lowering energy consumption by 15% through AI-driven optimization reduces operational expenses Equivalent products from the list include Siemens Digital Industries or DAIM Research →

-
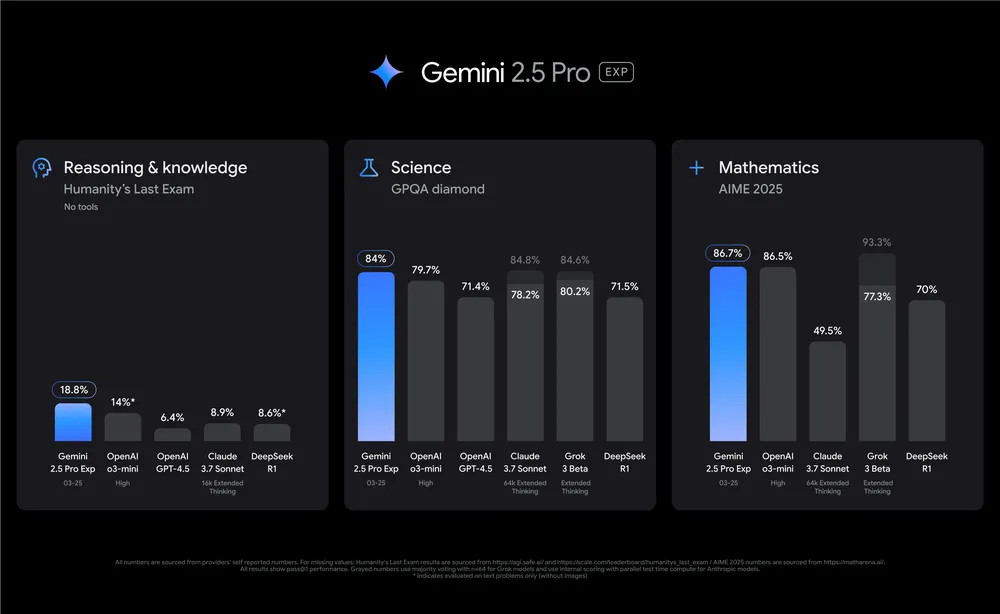
Google AI Released Gemini 2.5 Pro Experimental: An Advanced AI Model that Excels in Reasoning, Coding, and Multimodal Capabiliti…
Google AI Released Gemini 2.5 Pro Experimental: An Advanced AI Model that Excels in Reasoning, Coding, and Multimodal Capabilities In the evolving field of artificial intelligence, a significant challenge has been developing models that can effectively reason through complex problems, generate accurate code, and process multiple forms of data. Traditional AI systems often excel in… →
-
GTM 139: AI Agents Are Changing Everything — Microsoft’s VP of AI Agents on the New Era of Work and Software | Ray Smith
The GTM Podcast is available on any major directory, including: Apple Podcasts Spotify YouTube Ray Smith is the VP of AI Agents at Microsoft. Previously, he was the Global VP of Product for SAP, CRM and Sales Cloud. Before that, he was the CEO and Co-Founder of DataHug, which was acquired by Calidus Cloud in… →
-
Go-to-market strategy – Стратегия выхода на рынок. Как спланировать успешный запуск продукта, чтобы максимально эффективно донес…
Go-to-market strategy – Стратегия выхода на рынок. Как спланировать успешный запуск продукта, чтобы максимально эффективно донести его до целевой аудитории и начать привлекать пользователей. Важность правильной маркетинговой стратегии на старте. #ИИ #Продуктовыймененджмент #ИИМенеджмент #Менеджмент #Продукт →

-
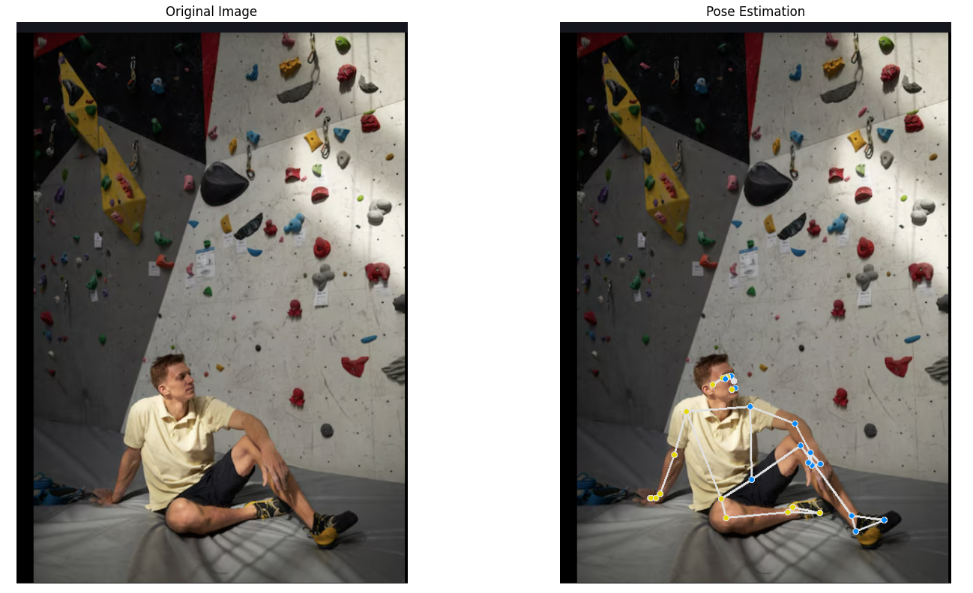
A Code Implementation for Advanced Human Pose Estimation Using MediaPipe, OpenCV and Matplotlib
A Code Implementation for Advanced Human Pose Estimation Using MediaPipe, OpenCV and Matplotlib Human pose estimation is a cutting-edge computer vision technology that transforms visual data into actionable insights about human movement. By utilizing advanced models like MediaPipe& BlazePose and powerful libraries such as OpenCV, developers can track body key points with unprecedented accuracy. In… →

-
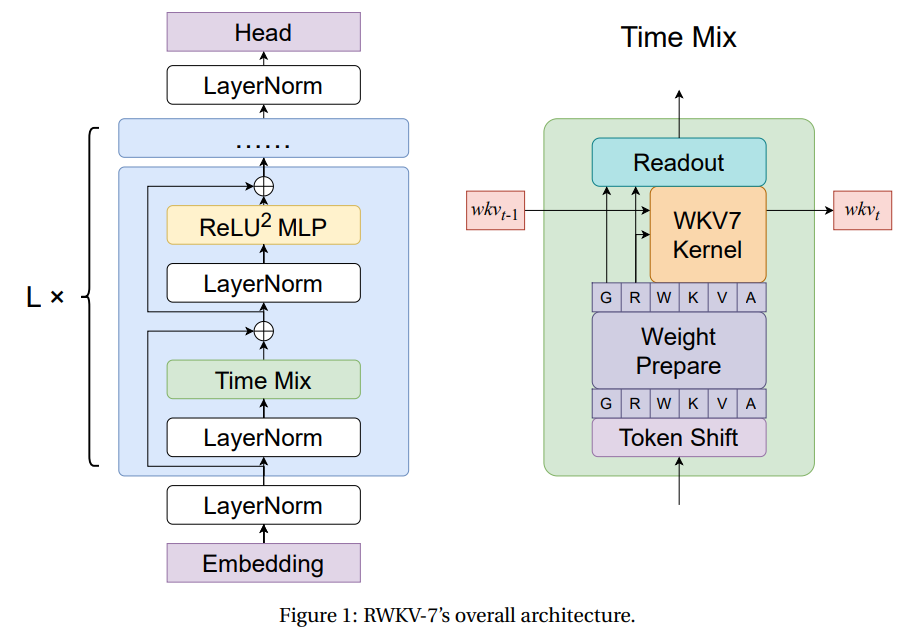
RWKV-7: Advancing Recurrent Neural Networks for Efficient Sequence Modeling
RWKV-7: Advancing Recurrent Neural Networks for Efficient Sequence Modeling Autoregressive Transformers have become the leading approach for sequence modeling due to their strong in-context learning and parallelizable training enabled by softmax attention. However, softmax attention has quadratic complexity in sequence length, leading to high computational and memory demands, especially for long sequences. While GPU optimizations… →
-
Effect of Plasma Air Purifiers on Infection Rates in Orthopedic Surgery
CONCLUSIONS: In modern operating rooms equipped with standard, midrange airflow ventilation systems, the addition of wall-mounted plasma air purifiers did not reduce the PSIM rate after orthopedic surgery. (Funded by the Swedish Research Council; grant number, 2017-00198; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT02695368.). →
-
A phase 2 study of adjuvant chemotherapy with 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin and oxaliplatin after lung metastasectomy for colorectal cancer (WJOG5810G)
CONCLUSIONS: Adjuvant chemotherapy with mFOLFOX6 is feasible, and may be effective after lung metastasectomy for colorectal cancer. →
-
Gamification – Геймификация. Использование игровых элементов и механик в неигровых продуктах для повышения вовлеченности. Как иг…
Gamification – Геймификация. Использование игровых элементов и механик в неигровых продуктах для повышения вовлеченности. Как игровые аспекты, такие как достижения, уровни или конкурсы, могут мотивировать пользователей и улучшить пользовательский опыт. #Продукт #Менеджмент #Маркетинг #ИИМенеджмент #Продуктовыймененджмент →

-
Zendesk – Система для управления заявками в поддержке. Применение: эффективное управление запросами клиентов и предоставление по…
Zendesk – Система для управления заявками в поддержке. Применение: эффективное управление запросами клиентов и предоставление поддержки через различные каналы. Бизнес-кейс: компания использует Zendesk для обработки клиентских запросов, что помогает улучшить скорость отклика и повысить удовлетворенность пользователей. #ИИМаркетинг #Продукт #Маркетинг #ИИМенеджмент #Продуктовыймененджмент →
