H Company Releases Holo1.5: An Open-Weight Computer-Use VLMs Focused on GUI Localization and UI-VQA
H Company, a French AI startup, has announced the release of Holo1.5, a family of open foundation vision models designed specifically for computer-use (CU) agents that interact with real user interfaces through screenshots and pointer/keyboard actions. The release includes models with 3B, 7B, and 72B parameters, demonstrating a documented ~10% accuracy improvement over the previous version, Holo1. The 7B model is licensed under Apache-2.0, while the 3B and 72B models carry research-only constraints from their upstream bases. Holo1.5 targets two essential capabilities for CU stacks: precise UI element localization (coordinate prediction) and UI visual question answering (UI-VQA) for state understanding.
Why Does UI Element Localization Matter?
UI element localization is critical as it allows an agent to convert user intent into pixel-level actions. For example, an instruction like “Open Spotify” requires predicting the clickable coordinates of the correct control on the current screen. Inaccuracies in this process can lead to failure, where a single misplaced click can disrupt a multi-step workflow. Holo1.5 has been trained and evaluated for high-resolution screens (up to 3840×2160) across desktop (macOS, Ubuntu, Windows), web, and mobile interfaces, enhancing its robustness in complex professional UIs where small targets increase error rates.
How is Holo1.5 Different from General VLMs?
General vision language models (VLMs) focus on broad grounding and captioning, while CU agents require dependable pointing and interface comprehension. Holo1.5 aligns its data and objectives specifically for CU applications, featuring large-scale supervised fine-tuning (SFT) on GUI tasks followed by reinforcement learning (GRPO-style) to enhance coordinate accuracy and decision reliability. The models are provided as perception components to be integrated into planners/executors (e.g., Surfer-style agents), rather than as complete end-to-end agents.
Performance on Localization Benchmarks
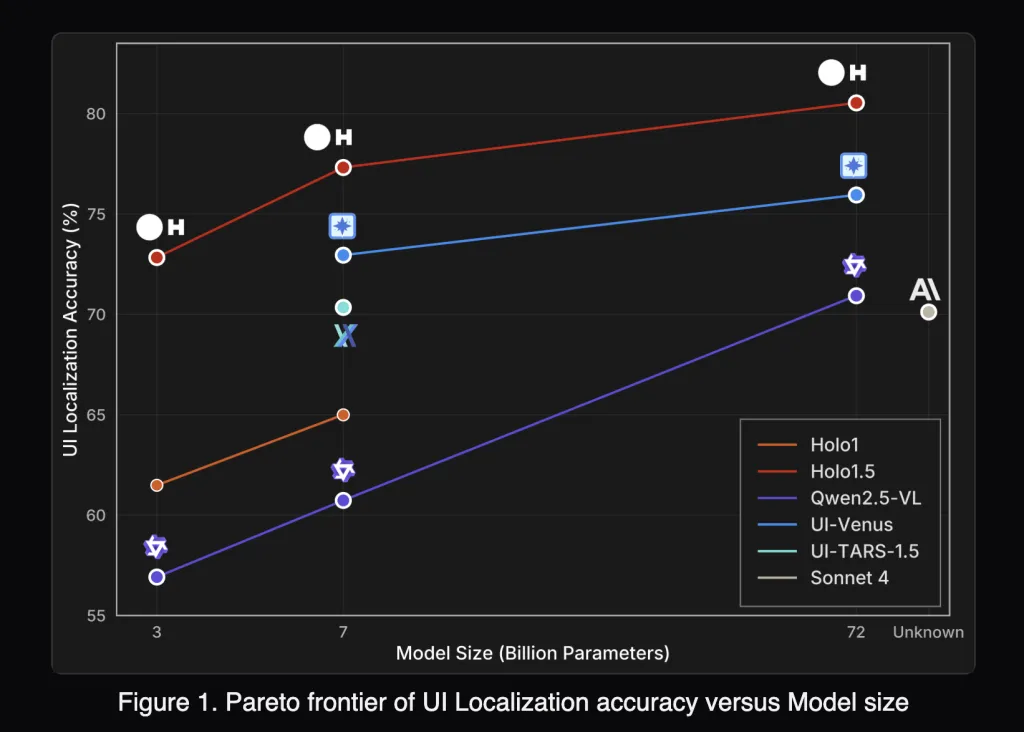
Holo1.5 has achieved state-of-the-art performance in GUI grounding across various benchmarks, including ScreenSpot-v2, ScreenSpot-Pro, GroundUI-Web, Showdown, and WebClick. The following are average scores for the 7B model:
- Holo1.5-7B: 77.32
- Qwen2.5-VL-7B: 60.73
On the ScreenSpot-Pro benchmark, which evaluates performance in professional applications with dense layouts, Holo1.5-7B scored 57.94 compared to 29.00 for Qwen2.5-VL-7B, indicating significantly better target selection under realistic conditions. The 3B and 72B models show similar relative improvements compared to their Qwen2.5-VL counterparts.
Improvements in UI Understanding (UI-VQA)
Holo1.5 also delivers enhancements in UI understanding, achieving consistent accuracy improvements on benchmarks like VisualWebBench, WebSRC, and ScreenQA (short/complex). The reported averages for the 7B model are approximately 88.17, with the 72B variant reaching around 90.00. This improvement is vital for agent reliability, allowing for clearer answers to queries such as “Which tab is active?” or “Is the user signed in?”, thereby reducing ambiguity and enhancing action verification.
Comparison with Specialized and Closed Systems
Under the published evaluation conditions, Holo1.5 outperforms open baselines (Qwen2.5-VL) and competitive specialized systems (e.g., UI-TARS, UI-Venus), while also demonstrating advantages over closed generalist models (e.g., Claude Sonnet 4) in the specified UI tasks. Practitioners should replicate these evaluations with their specific setups before making deployment-level conclusions, as protocols, prompts, and screen resolutions can affect outcomes.
Integration Implications for CU Agents
Holo1.5’s improved accuracy leads to:
- Higher click reliability at native resolution, particularly in complex applications such as IDEs, design suites, and admin consoles.
- Stronger state tracking, with enhanced detection of logged-in states, active tabs, modal visibility, and cues for success or failure.
- A pragmatic licensing path: the 7B model (Apache-2.0) is ready for production use, while the 72B checkpoint remains research-only, suitable for internal experimentation.
Positioning Holo1.5 in a Modern Computer-Use (CU) Stack
Holo1.5 functions as the screen perception layer within a CU stack:
- Input: Full-resolution screenshots (with optional UI metadata).
- Outputs: Target coordinates with confidence scores and brief textual answers regarding screen state.
- Downstream: Action policies that convert predictions into click/keyboard events, while monitoring verifies post-conditions and triggers retries or fallbacks.
Conclusion
Holo1.5 effectively narrows the practical gap in CU systems by combining strong coordinate grounding with concise interface understanding. For businesses seeking a commercially viable foundation today, the Holo1.5-7B model (Apache-2.0) offers an excellent starting point. Benchmarking on specific screens and implementing it within your planner and safety layers is highly recommended.
For further information, check out the Holo1.5 models on Hugging Face and explore the technical details. You can also visit our GitHub Page for Tutorials, Codes, and Notebooks. Stay updated by following us on Twitter and joining our ML SubReddit community with over 100,000 members, and don’t forget to subscribe to our newsletter.